Israel
Also known as: Isrāʾīl, Medinat Yisraʾel, State of Israel
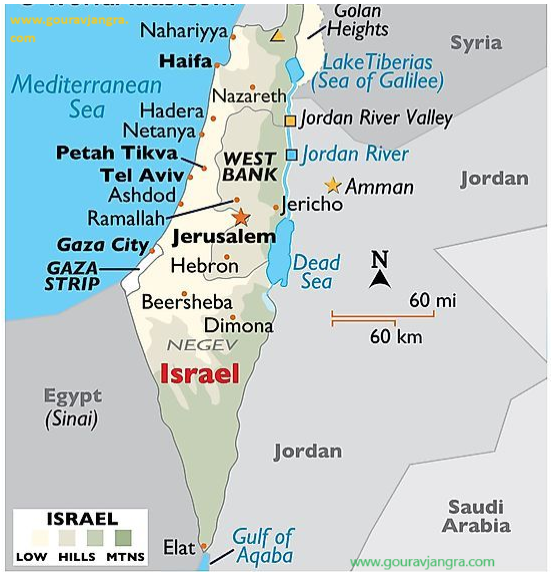
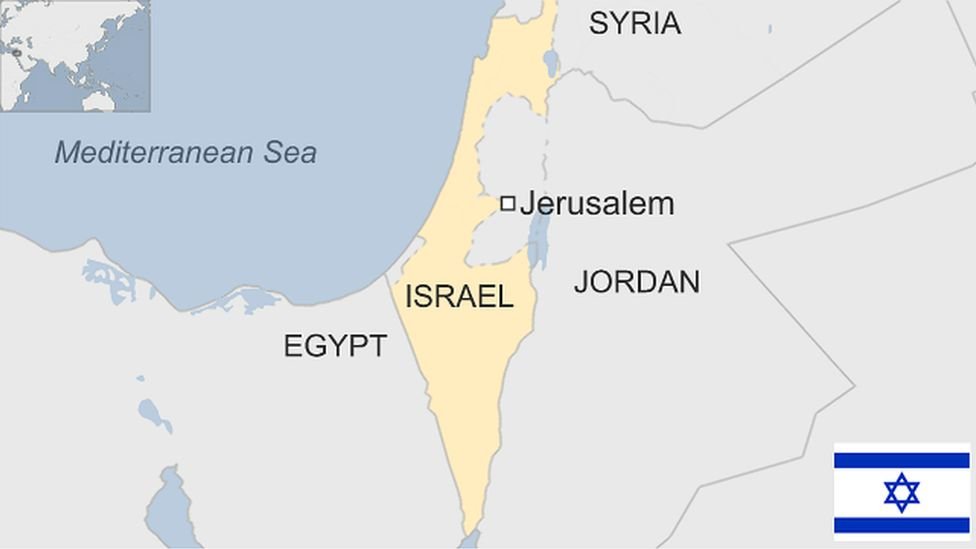
Israel, country in the Middle East, located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bounded to the north by Lebanon, to the northeast by Syria, to the east and southeast by Jordan, to the southwest by Egypt, and to the west by the Mediterranean Sea. Jerusalem is the seat of government and the proclaimed capital, although the latter status has not received wide international recognition.
Arabic: Isrāʾīl
Officially: State of Israel or Hebrew: Medinat Yisraʾel
Head Of Government: Prime Minister: Benjamin Netanyahu
Capital (Proclaimed): Jerusalem; international recognition of its capital status has largely been withheld.
Population: (2024 est.) 9,177,0001
Currency Exchange Rate: 1 USD equals 3.653 Israeli shekel
Head Of State: President: Isaac Herzog
Israel is a small country with a relatively diverse topography, consisting of a lengthy coastal plain, highlands in the north and central regions, and the Negev desert in the south. Running the length of the country from north to south along its eastern border is the northern terminus of the Great Rift Valley.
The State of Israel is the only Jewish nation in the modern period, and the region that now falls within its borders has a lengthy and rich history that dates from prebiblical times. The area was a part of the Roman Empire and, later, the Byzantine Empire before falling under the control of the fledgling Islamic caliphate in the 7th century CE. Although the object of dispute during the Crusades, the region, then generally known as Palestine, remained under the sway of successive Islamic dynasties until the collapse of the Ottoman Empire at the end of World War I, when it was placed under British mandate from the League of Nations.
Even before the mandate, the desire for a Jewish homeland prompted a small number of Jews to immigrate to Palestine, a migration that grew dramatically during the second quarter of the 20th century with the increased persecution of Jews worldwide and subsequent Holocaust perpetrated by Nazi Germany. This vast influx of Jewish immigrants into the region, however, caused tension with the native Palestinian Arabs, and violence flared between the two groups leading up to the United Nations plan to partition Palestine into Jewish and Arab sectors and Israel’s ensuing declaration of statehood on May 14, 1948.
“Israel Country Map”
Israel fought a series of wars against neighbouring Arab states during the next 35 years, which have resulted in ongoing disputes over territory and the status of refugees. Despite continuing tensions, however, Israel concluded peace treaties with several neighbouring Arab states during the final quarter of the 20th century.
Land
Relief
Despite its small size, about 290 miles (470 km) north-to-south and 85 miles (135 km) east-to-west at its widest point, Israel has four geographic regions—the Mediterranean coastal plain, the hill regions of northern and central Israel, the Great Rift Valley, and the Negev—and a wide range of unique physical features and microclimates.
“Israel Outline Map”
The Great Rift Valley, a long fissure in Earth’s crust, begins beyond the northern frontier of Israel and forms a series of valleys running generally south, the length of the country, to the Gulf of Aqaba. The Jordan River, which marks part of the frontier between Israel and Jordan, flows southward through the rift from Dan on Israel’s northern frontier, where it is 500 feet (152 metres) above sea level, first into the Ḥula Valley (Hebrew: ʿEmeq HaḤula), then into the freshwater Lake Tiberias, also known as the Sea of Galilee (Hebrew: Yam Kinneret), which lies 686 feet (209 metres) below sea level. The Jordan continues south along the eastern edge of the West Bank—now through the Jordan Valley (Hebrew: ʿEmeq HaYarden)—and finally into the highly saline Dead Sea, which, at 1,312 feet (400 metres) below sea level, is the lowest point of a natural landscape feature on the Earth’s surface. South of the Dead Sea, the Jordan continues through the rift, where it now forms the ʿArava Valley (Hebrew: “savannah”), an arid plain that extends to the Red Sea port of Eilat.
The sparsely populated Negev comprises the southern half of Israel. Arrow-shaped, this flat, sandy desert region narrows toward the south, where it becomes increasingly arid and breaks into sandstone hills cut by wadis, canyons, and cliffs before finally coming to a point where the ʿArava reaches Eilat.
Drainage
The principal drainage system comprises Lake Tiberias and the Jordan River. Other rivers in Israel are the Yarqon, which empties into the Mediterranean near Tel Aviv; the Qishon, which runs through the western part of the Plain of Esdraelon to drain into the Mediterranean at Haifa; and a small section of the Yarmūk, a tributary of the Jordan that flows west along the Syria-Jordan border. Most of the country’s remaining streams are ephemeral and flow seasonally as wadis. The rivers are supplemented by a spring-fed underground water table that is tapped by wells. Israel has a chronic water shortage, and its hydraulic resources are fully utilized: about three-fourths for irrigation and the remainder for industrial and household water use.
Soils
The coastal plain is covered mainly by alluvial soils. Parts of the arid northern Negev, where soil development would not be expected, have windblown loess soils because of proximity to the coastal plain. The soils of Galilee change from calcareous rock in the coastal plain, to Cenomanian and Turonian limestone (deposited from about 99 to 89 million years ago) in Upper Galilee, and to Eocene formations (those dating from about 55 to 35 million years ago) in the lower part of the region. Rock salt and gypsum are abundant in the Great Rift Valley. The southern Negev is mainly sandstone rock with veins of granite.
Climate of Israel
Israel has a wide variety of climatic conditions, caused mainly by the country’s diverse topography. There are two distinct seasons: a cool, rainy winter (October–April) and a dry, hot summer (May–September). Along the coast, sea breezes have a moderating influence in summer, and the Mediterranean beaches are popular. Precipitation is light in the south, amounting to about 1 inch (25 mm) per year in the ʿArava Valley south of the Dead Sea, while in the north it is relatively heavy, up to 44 inches (1,120 mm) a year in the Upper Galilee region. In the large cities, along the coastal plain, annual rainfall averages about 20 inches (508 mm) per year. Precipitation occurs on about 60 days during the year, spread over the rainy season. Severe summer water shortages ensue in years when the rains come late or rainfall totals are less than normal.
Average annual temperatures vary throughout Israel based on elevation and location, with the coastal areas adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea having milder temperatures—ranging from about 84 °F (29 °C) in August to about 61 °F (16 °C) in January—and higher rates of humidity than areas inland, especially during the winter. Likewise, higher elevations, such as Upper Galilee, have cool nights, even in summer, and occasional snows in the winter. However, the coastal city of Eilat, in the south, despite its proximity to the Red Sea, is closer to the climate of the Jordan and ʿArava valleys and the Negev, which are hotter and drier than the northern coast; there, daytime temperatures reach about 70 °F (21 °C) in January and may rise as high as 114 °F (46 °C) in August, when the average high is 104 °F (40 °C).
Plant and animal life
Natural vegetation is highly varied, and more than 2,800 plant species have been identified. The original evergreen forests, the legendary “cedars of Lebanon,” have largely disappeared after many centuries of timber cutting for shipbuilding and to clear land for cultivation and goat herding; they have been replaced by second-growth oak and smaller evergreen conifers. The hills are mostly covered by maquis, and wildflowers bloom profusely in the rainy season. Only wild desert scrub grows in the Negev and on the sand dunes of the coastal plain. North of Beersheba, most of the country is under cultivation or is used for hill grazing. Where irrigation is available, citrus groves, orchards of subtropical fruit, and food crops flourish. Millions of trees have been planted through a government reforestation program.
Animal life is also diverse. Mammals include wildcats, wild boars, gazelles, ibex, jackals, hyenas, hares, coneys, badgers, and tiger weasels. Notable among the reptiles are geckos and lizards of the genus Agama and vipers such as the carpet, or saw-scaled, viper (Echis carinatus). More than 400 species of birds have been identified in the region, including the partridge, tropical cuckoo, bustard, sand grouse, and desert lark. There are many kinds of fish and insects, and locusts from the desert sometimes invade settled areas. Several regions have been set aside as nature reserves, notably parts of the ʿArava in the south and Mount Carmel, Mount Meron, and the remains of the Ḥula Lake and marshes in the north. The Mediterranean coast and the Jordan and ʿArava valleys are important routes for migratory birds.
Settlement patterns
Jewish immigration in the 20th century greatly altered the settlement pattern of the country. The first modern-day Jewish settlers established themselves on the coastal plain in the 1880s.

“Settlement Patterns”
Later they also moved into the valleys of the interior and into parts of the hill districts, as well as into the Negev. Small cities such as Haifa and Jerusalem grew in size, and the port of Jaffa (Yafo) sprouted a suburb, Tel Aviv, which grew into one of the largest cities in Israel. Jewish immigrants also settled those areas of the coastal plain, the Judaean foothills, and the Jordan and ʿArava valleys evacuated by Palestinians during the war of 1948, thereby becoming the majority in many areas previously inhabited by Arabs. Although the majority of the Bedouin of the Negev left the region when Israel incorporated the territory, the desert has continued to be largely the domain of the Arab nomads who remained or returned following the end of fighting.
The non-Jewish population is concentrated mainly in Jerusalem (about one-fifth of the residents of the city), and in the north, where Arabs constitute a substantial part of the population of Galilee.
Jerusalem, perched high among the Judaean hills, is one of the great cities of the world, with a long history, unique architecture, and rich archeological heritage. It is the capital of Israel, and its walled “Old City” is divided into four quarters—Muslim, Jewish, Christian, and Armenian—symbolizing its spiritual significance to the region’s major religious and ethnic groups.
Rural settlement
The rural population, defined as residents of settlements with less than 2,000 people, amounts to less than one-tenth of the nation’s total inhabitants. About one-tenth of the Jewish population is rural, of whom more than half are immigrants who arrived after 1948. The Jewish rural settlements are organized into kibbutzim (2 percent of the total population), which are collective groups voluntarily practicing joint production and consumption; moshavim (3 percent), which are cooperatives of small holders who practice joint sales and purchases, make common use of machinery, minimize hired labour, and lease national land; and agricultural communities or individually owned farms engaged in private production. The kibbutzim and moshavim pioneered settlement in underdeveloped areas, performed security functions in border areas, and contributed substantially to the nation’s ability to absorb new immigrants in the early years of the state.

Jerusalem – Damascus Gate
Only a tiny fraction of the Arab population lives in rural areas. Those who do are divided between the Bedouin and residents of small agricultural villages. Many such communities are now defined as urban by the Israeli government because their populations exceed 2,000, despite the fact that some residents still engage in agriculture. Before 1948 Jewish and Arab agricultural settlements existed side by side but were largely independent of each other. Since then, however, thousands of Arabs from the Gaza Strip and the Israeli-occupied territory of the West Bank have found employment in Israel in the citrus groves or in industry or as construction labourers. This ready labour pool, together with increased agricultural mechanization, has led to a drop in the number of Jewish agricultural workers. In Arab villages, fewer than half of the adult labourers, both men and women, are engaged in working the land.
There has been a growing tendency among farmers to practice intensive cultivation, to diversify crops, and to shift from small holdings to large farms. Most of the remaining Arab farmers work their own land, although some either lease land or work for Arab or Jewish landlords. Many Bedouin also have abandoned herding for work in towns and cities, establishing residence in permanent settlements that continue to maintain traditional tribal identity.
Urban settlement
The great majority of the population, both Jewish and Arab, reside in urban areas. As the industrial and service sectors of the economy have grown, the two large conurbations of Tel Aviv–Yafo and Haifa, along the coastal plain, have come to house more than half of the country’s population. The government has made great efforts to prevent the population from becoming overconcentrated in these areas, overseeing in both the north and south the development of new towns occupied largely by the country’s most recent immigrants. These towns serve as centres of regional settlement and fulfill specialized economic functions, such as the manufacture of textiles, clothing, machinery, electronic equipment, and computer software. One such place, Beersheba, in the northern Negev, grew from a planned new town founded on a small older settlement in the 1950s into a city, the result of waves of Jewish immigrants from North Africa and the former Soviet Union.
The major urban centres inhabited by Arabs include cities and towns with both Arab and Jewish populations—such as Jerusalem, Haifa, ʿAkko, Lod, Ramla, and Yafo—and towns with predominantly Arab populations, including Nazareth in Galilee, where a mainly Jewish suburb is nearly equal in population to the Arab city. Many of the former differences in ways of life between Arabs and Jews are diminishing in towns with mixed populations, even though each group usually lives in different quarters.
People of Israel
Religious and ethnic groups
Jews constitute about three-fourths of the total population of Israel. More than one-fifth of the population consists of Arabs, almost all of whom are Palestinians from Sunni Muslim (roughly three-fourths) or Christian communities. Druze and other ethnic Arabs who do not consider themselves Palestinians make up a small fraction of the total population..
Israel Ethnic Composition (2023)
Israel Ethnic Composition (2022)
Israel Ethnic Composition (2021)
Israel Ethnic Composition (2020)
Israel Ethnic Composition (2019)
Israel Ethnic Composition (2018)
Jews
The Jewish population is diverse. Jews from eastern and western Europe, the Middle East and North Africa, Central Asia, North America, and Latin America have been immigrating to this area since the late 19th century. Differing in ethnic origin and culture, they brought with them languages and customs from a variety of countries. The Jewish community today includes survivors of the Holocaust, offspring of those survivors, and émigrés escaping anti-Semitism. The revival of Hebrew as a common language and a strong Israeli national consciousness have facilitated the assimilation of newcomers to Israel but not completely eradicated native ethnicities. For example, religious Jews immigrating to Israel generally continue to pray in synagogues established by their respective communities.
Religious Jews in Israel constitute a significant and articulate section of the population. As such, they are often at odds with a strong secular sector that seeks to prevent religious bodies and authorities from dominating national life. The two main religious-ethnic groupings are those Jews from central and eastern Europe and their descendants who follow the Ashkenazic traditions and those Jews from the Mediterranean region and North Africa who follow the Sephardic. There are two chief rabbis in Israel, one Ashkenazi and one Sephardi. Tension is frequent between the two groups, largely because of their cultural differences and the social and political dominance of the Ashkenazim in Israeli society. Until recently, it was generally true that the Sephardim tended to be poorer, less educated, and less represented in higher political office than the Ashkenazim.
Karaites
The Karaites are a Jewish sect that emerged in the early Middle Ages. Several thousand members live in Ramla, and more recently in Beersheba and Ashdod. Like other religious minorities, they have their own religious courts and communal organizations. Considered part of Jewish society, they have maintained their separate identity by resisting intermarriage and preserving their religious rites based on the Torah as the sole source of religious law.
Samaritans
Samaritans trace their roots to those Jews not dispersed when the Assyrians conquered Israel in the 8th century BCE. About half of the few hundred surviving members of the Samaritan community live near Tel Aviv in the town of Holon. The rest live on Mount Gerizim (Arabic: Jabal al-Ṭūr), near Nablus in the West Bank. They preserve their separate religious and communal organizations and speak Arabic but pray in an archaic form of Hebrew. They participate in national life as part of the Jewish section of the population.
Arabs
Arabs constitute the largest single minority in Israel, and, though most are Muslims of the Sunni branch, Arab Christians form a significant minority, particularly in the Galilee region in northern Israel. Arabs, whether Christian, Muslim, or Druze, speak Levantine Arabic and learn Modern Standard Arabic in school. An increasing number also avail themselves of higher education within Israel’s public schools and colleges, and many younger Arabs are bilingual in Hebrew. They are full Israeli citizens with political and civil rights that are equal to those of Israel’s Jewish citizens, with the exception of some limitations on military service. Many Arabs participate actively in the Israeli political process, and several Arab political parties have members in the Israeli Knesset. Despite these inclusive rights, the Jewish character enshrined in state symbols and values and the broad disparities between Jewish and Arab communities has left many Arabs feeling excluded and disadvantaged.
Most Arabs are Palestinians, and no broad agreement exists on how best to refer to that particular community. They are commonly called Israeli Arabs or Arab Israelis, following the legal designation according to ethnicity, and many of Israel’s Palestinian citizens embrace this more legally defined term. However, many are wary that this label overlooks their Palestinian identity and prefer terms that assert that identity, such as “Palestinians inside [Israel]” (Arabic: filasṭīniyyū al-dākhil). Members of the community sometimes emphasize Israeli citizenship, especially when asserting their rights to equal treatment under the law. A popular descriptor, “Palestinian citizens of Israel,” acknowledges both Palestinian identity and participation in Israel’s socio-political framework.
Muslims
The overwhelming majority of Israel’s Muslims are Arabs. Like all other religious communities, Muslims enjoy considerable autonomy in dealing with matters of personal status. They have separate religious courts for issues such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance. The state oversees their religious institutions. Israel’s Bedouin, roughly one-tenth of the Arab population, are exclusively Muslim.
Christians
Most Christians in Israel are Arabs, and Christian communities in Israel, regardless of ethnicity, have a wide degree of autonomy in religious and communal affairs. The Greek Catholic and Greek Orthodox churches are the largest denominations, and most of them are found in Jerusalem. Apart from the Greek Orthodox church, which has a patriarchate in Jerusalem, each church is dependent to a degree on a supreme hierarch abroad. These communities include Roman Catholics and Uniates (Melchites, Maronites, Chaldean Catholics, Syrian Catholics, and Armenian Catholics). Jerusalem also has a Russian Orthodox community. The Evangelical, Episcopal, and Lutheran churches are small and primarily Arabic-speaking.
Druze
The Druze, who live in villages in Galilee and around Mount Carmel, have traditionally formed a closed tight-knit community and practice a secretive religion founded in 11th-century Fatimid Egypt. Though Israeli Druze maintain contact with coreligionists in Lebanon and Syria, members of each group adhere to the authority of their country of residence. Israel has recognized the Druze as a separate Arab community since 1957, and Israeli Druze serve in the armed forces. Druze have traditionally been agriculturists, but younger members have found employment throughout the economy.
Other groups:-
The Bahāʾī faith, a universal religion founded in Iran in the mid-19th century, is the only religion other than Judaism to have its world centre in Israel. A teaching centre, archive building, shrine, and administrative headquarters are located on Mount Carmel in Haifa. There are a few hundred adherents in Israel, most of whom are employed at the centre in Haifa.
The Circassians, who are Sunni Muslims, emigrated from the Caucasus in the 1870s. They number a few thousand and live in villages in Galilee, preserving their native language and traditions. Older Circassians speak Arabic as well as the Circassian language, but members of the younger generation speak Hebrew. The men serve in the Israeli armed forces.
Demographic trends
The most significant demographic issue in Israel since its establishment has been Jewish immigration. In 1948 the Jewish population of Israel was about 670,000; this number increased to more than 1,000,000 the next year as a result of immigration. Between 1949 and 1997 about 2,350,000 Jewish immigrants entered the country; about 700,000 to 750,000 Jews left it, although some later returned. The total number of immigrants includes more than 320,000 Soviet Jews who came to Israel in 1989–91 and continued to arrive at the rate of about 50,000 per year for the next decade. Nearly 28,000 Ethiopian Jews immigrated in 1990–92, adding to an earlier migration of 11,000 in 1984–85; after additional migrations, the number of Ethiopian Jews in Israel numbered nearly 150,000 in 2020. The largest proportion of Jews trace their roots to Europe (including the former Soviet Union) and North America, though some also hail from Africa (mostly North Africa), Asia, and the Middle East.
More than half of the Arab population fled their homes during the war of 1948, of whom only a small fraction were allowed to return after the end of hostilities. While the Jewish population has grown more from immigration than from natural increase since that time, the Arab population has grown mainly through high birth rates, which were markedly higher than among Israel’s Jews for decades, and through the addition of about 66,000 residents of East Jerusalem, captured from Jordan in 1967 and later annexed by Israel. Overall, the population is youthful, with about one-fourth being 15 years old or younger. Life expectancy is among the highest in the world: some 85 years for women and 81 years for men.
Israel age breakdown(2023)
- Age(Range)
- Percentage
- Age(Range)
- Percentage
Economy of Israel
The large influx of well-trained and Western-educated European and North American immigrants contributed greatly to a rapid rise in Israel’s gross national product (GNP) after 1948. Although most of them had to change occupations, a nucleus of highly skilled labour, in combination with the country’s rapid founding of universities and research institutes, facilitated economic expansion. The country obtained large amounts of capital, which included gifts from Jews around the world, reparations from the Federal Republic of Germany for Nazi crimes, grants-in-aid from the U.S. government, and capital brought in by immigrants. Israel has supplemented these forms of revenue with loans, commercial credits, and foreign investment.
The goals of Israel’s economic policy are continued growth and the further integration of the country’s economy into world markets. Israel has made progress toward these goals under difficult conditions, such as a rapid population increase, a boycott by most Arab countries, heavy expenditure on defence, a scarcity of natural resources, high rates of inflation, and a small domestic market that limits the economic savings of mass production. Despite these obstacles, Israel has achieved a high standard of living for most of its residents, the growth of substantial industrial export and tourism sectors, and world-class excellence in advanced technologies and science-based industry. However, this economic progress has not been uniform. Israeli Arabs are generally at the lower rungs of the economic ladder, and there are substantial economic divisions among Israeli Jews, mainly between the Sephardim and Ashkenazim.
Large influxes of capital have passed through government channels and public organizations and enlarged that sector of the economy that engages in enterprises between the government and private concerns. Government policy dating from the late 1970s, however, has been directed toward privatization. The private, governmental, and, to a limited extent, cooperative sectors all coexist in an economy that supports both the broad objectives of state policy and individual enterprise.
Tax rates in Israel are among the highest in the world, with income, value-added, customs and excise, land, and luxury taxes being the main sources of revenue. The government has gradually raised the proportion of indirect taxes since the late 1950s. Tax reforms in 1985 included a new corporate tax levied on previously untaxed business sectors while slightly reducing direct taxes on individuals. Taxation approaches two-fifths of the value of GNP and is about one-fourth of average household income.
The General Federation of Labour in Israel (Histadrut) is the largest labour union and voluntary organization in the country. It once was also one of the largest employers in Israel and owner or joint owner of a wide range of industries, but by the mid-1990s it had sold most of its holdings to private investors. Since 1960 Arab workers have been admitted to the organization with full membership rights. The Manufacturers’ Association of Israel and the Farmers’ Union represent a large number of the country’s employers.
Education
Schooling is obligatory and free for children between the ages of 5 and 15 and free, but not compulsory, for those 16 and 17. Young people between the ages of 14 and 18, however, who have not completed secondary schooling are obliged to attend special classes. Parents may choose to send children to state secular schools, state religious schools, or private religious schools. For Arab students, there is a system of schools in which Arabic is the primary language of instruction. The school syllabus is supplemented by radio and television educational programming in both Hebrew and Arabic. The educational system gives special attention to agricultural and technical training. Adult education for immigrants assists in their cultural integration.
In addition to the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (1925), the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa (1924), and the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot (1934), several institutions of higher learning have been founded since 1948, including the universities of Tel Aviv and Haifa, Bar-Ilan University (religious, located near Tel Aviv), and Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba. The Open University of Israel (formerly Everyman’s University) in Tel Aviv opened in 1974, and teachers’ training colleges include two for Arabs. The language of instruction at Israeli universities is Hebrew, while the teaching system represents a mixture of European and American methods. In the 1990s a number of regional community colleges were established, and several foreign universities began offering specialized professional degrees in fields such as law, business, and education. Academic freedom in the universities is protected by Israeli law.











